

Driving While High on Marijuana
DUIs can involve drugs like marijuana — not just alcohol.
Compare quotes from top providers

In all but three states, marijuana usage is legal in some form, be it for regulated medical use or recreational. But even in states where using marijuana is 100 percent legal for adults, driving while impaired by marijuana is still illegal everywhere. That said, some states allow people to drive if they have low levels of tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) detected in their bodies, but are not “impaired,” while other states have a zero-tolerance law.
Keep reading to learn about your state’s laws surrounding marijuana usage and driving, as well as the effects that smoking, vaping or ingesting marijuana can have when you get behind the wheel.
Laws About Driving While High on Marijuana

State laws surrounding marijuana usage and driving fall into one of four categories, according to the National Conference of State Legislatures:
- Zero tolerance: It is illegal to drive with any amount of THC or metabolites in your body.
- Per se law: You cannot drive with amounts of THC above the legal limit, which varies by state.
- Under the influence DUID: You cannot drive while under the influence or affected by THC, although there’s no exact threshold for impairment.
- Permissible inference law: A driver is considered “under the influence” of marijuana if the amount of THC in their blood is 5 ng/ml or higher.1
NOTE
THC is the major psychoactive component in cannabis. The Federal Drug Administration classifies THC as a Schedule 1 drug.2
Laws and Penalties by State
See below for your state’s impaired driving law, as well as penalties for first offenses of driving while impaired from using marijuana, a specific type of DUI.
| State | Law governing driving after using marijuana | Penalties for the first offense |
|---|---|---|
| Alabama | Under the influence DUID | Imprisonment for up to 1 year and/or
fine between $600 to $2,100 License suspension: 90 days Ignition interlock device required for 6 months following reinstatement or 2 years if there was a child under the age of 14 in the vehicle |
| Alaska | Under the influence DUID | Jail/monitoring time: 72 consecutive hours
Fine: $1,500 Ignition interlock device: 6 months Cost of imprisonment for offenses after 7/9/19: $330 License revocation: 90 days |
| Arizona | Zero tolerance law | Jail: 10 consecutive days maximum
Fine: $1,250 minimum Required drug education/treatment Must have ignition interlock device Must perform community service |
| Arkansas | Under the influence DUID | License suspension: 6 months
Must complete a drug treatment or education program, victim impact panel class Reinstatement fee: $150 |
| California | Under the influence DUID | Suspended or revoked license
Must complete a DUI program, file an SR-22, pay license reissue/restriction fees and install an ignition interlock device Imprisonment: Up to 6 months Fine: Amount not specified Impoundment: Possible and may include storage fee |
| Colorado | Permissible inference law; driver is considered under the influence if their THC levels are 9 ng/ml or higher, but drivers can introduce an affirmative defense arguing they were not impaired | DUI (driving under the influence): 5 days to 1 year in jail, fine between $600 to $1,500 or both
DWAI (driving while ability impaired): 2 days to 1 year in jail, fine between $200 to $1,500 or both |
| Connecticut | Under the influence DUID | License suspension: 45 days
Ignition interlock device: 1 year following restoration |
| Delaware | Under the influence DUID | $500 to $1,500 fine and/or 1 year of imprisonment maximum |
| Florida | Under the influence DUID | Fine: $500 to $1,000
Imprisonment: 6 months maximum Impoundment of vehicle: 10 days, unless the family of the defendant has no other transportation License revocation: 180 days to 1 year if no bodily injury, minimum 3 years if bodily injury Must complete DUI school |
| Georgia | Zero tolerance law | Fine: $300 to $1,000
Imprisonment: 10 days to 12 months, plus probation Community service: 40 hours maximum Completion of a Drug Use Risk Reduction Program |
| Hawaii | Under the influence DUID | Substance abuse rehabilitation program: 14 hours minimum
License revocation: 1 year to 18 months Ignition interlock device One of the following: Community service: 72 hours Imprisonment: 2 to 5 days Fine: $250 to $1,000 Surcharge: $25, either to the neurotrauma special fund or trauma system special fund |
| Idaho | Under the influence DUID | Jail: 6 months maximum
Fine: $1,000 maximum License suspension: 30 days required, plus anywhere from 15 to 60 days but can have restricted driving privileges during this time Ignition interlock device: 1 year following license reinstatement |
| Illinois | Per se law; limit is either 5 ng/mg for THC or 10 ng/mg for delta-9 THC | Community service: 100 hours minimum
Fine: $500 minimum |
| Indiana | Zero tolerance law | Court costs and fees: Must pay anything over $300
Jail: 1 year maximum Fine: $5,000 maximum License suspension: Up to 2 years or probation and required to enroll in a substance abuse education course and license suspension for 30 days, then a 180-day probation (can only drive for work purposes) Victim impact panel, urine drug testing; other terms of probation may be required |
| Iowa | Zero tolerance law | Imprisonment: 2 days to 1 year, less any time spent in a drug program with law enforcement security
Fine: $1,250 but can waive up to $625 of fine if there was no personal or property injury Community service: May be required License revocation: 180 days to 1 year Ignition interlock device: During restricted license Substance abuse evaluation and treatment required |
| Kansas | Under the influence DUID | 1 year maximum of imprisonment, $100 to $500 fine or both |
| Kentucky | Under the influence DUID | Substance abuse program: 90 days
License suspension: 6 months but can be reduced to 4 months with an ignition interlock device for 90 days |
| Louisiana | Under the influence DUID | Imprisonment: 10 days mandatory, up to 6 months
Fine: $3,000 to $1,000 May require probation, community service and participation in a substance abuse/driver improvement program instead of mandatory sentence License suspension: 90 days |
| Maine | Under the influence DUID | Fine: $500 minimum, or, if a person didn’t submit an alcohol test, $600 minimum
License suspension: 150 days Imprisonment: At least 2 days or at least 4 days if person failed to submit to the test |
| Maryland | Under the influence DUID | 2 months maximum imprisonment; fine of less than $500 or both |
| Massachusetts | Under the influence DUID | Fine of $500 to $5,000, imprisonment of less than 2.5 years or both
$300 total in assessment fees |
| Michigan | Zero tolerance law | Fine: $500 maximum
Imprisonment: 93 days maximum Community service: 360 hours maximum License suspension: 180 days maximum Points on driver’s license: 6 |
| Minnesota | Under the influence DUID | 90 days maximum of imprisonment, $1,000 fine or both
Driver’s license revocation for 3 months to 6 years May also lose license plate/car |
| Mississippi | Under the influence DUID | Fine of $250 to $1,000, imprisonment of 2 days maximum or both
May replace imprisonment with a victim impact panel Driver’s license suspension: 90 days minimum but can get a restricted license for work/school/medical care after 30 days from the suspension effective date |
| Missouri | Under the influence DUID | License suspension: 90 days but may be eligible for restricted license the entire time or for 60 days
Imprisonment: 6 months maximum Fine: $500 maximum |
| Montana | Under the influence DUID | Imprisonment: 2 days to 6 months
Fine: $600 to $1,000 If there was 1 or more passenger under 16 years old: Imprisonment: 2 days to 1 year Fine: $1,200 to $2,000 |
| Nebraska | Under the influence DUID | License revocation: 6 months
Ignition interlock required until end of probation Fine: $500 |
| Nevada | Per se law; felony violations at 2 ng/ml for THC and 5 ng/mg for THC metabolite | Imprisonment: 2 days to 6 months
Fine: $400 to $1,000, plus $121 reinstatement fee, $35 victims compensation civil penalty, $42.25 driver’s license fee, $26 testing fee Chemical test fee: $60 Substance abuse treatment Victim impact panel Must use ignition interlock device upon license reinstatement Must pass driver’s license test SR-22: 3 years |
| New Hampshire | Under the influence DUID | Impaired Driver Care Management Program (IDCMP): Must complete intake/screening. If screening is negative, will have to take an Impaired Driver Education Program (IDEP) or a Weekend Impaired Driver Education Program (WIDEP) and will need a complete substance use disorder evaluation within 30 days of conviction
If screening is positive, IDCMP will create a service plan If someone doesn’t comply, their license and driving privileges will be revoked until they comply Fine: $500 minimum Driver’s license revocation: 9 months to 2 years |
| New Jersey | Under the influence DUID | Fine: $300 to $500
Imprisonment: 30 days maximum Driver’s license revocation or suspension: 7 months to 1 year Other fines: $225 May require participation in a supervised visitation program as either a condition of probation or a form of community service |
| New Mexico | Under the influence DUID | Imprisonment: 90 days maximum, fine of $999 maximum or both
Probation: 90 days to 1 year Community service: 24 hours minimum Fine: $300 Must complete a screening program/driver drug rehabilitation program |
| New York | Under the influence DUID | Fine: $500 to $1,000
Imprisonment: 1 year maximum License revocation: 6 months minimum |
| North Carolina | Under the influence DUID | License revocation: 1 year |
| North Dakota | Under the influence DUID | Fine: $500 to $750
Imprisonment: 2 days License suspension: 91 to 180 days Additional evaluation required |
| Ohio | Per se law; cannot have more than 25 ng/ml of delta-9 THC in urine or at least 5 ng/ml in whole blood | Imprisonment: 3 days mandatory, 6 months maximum
Fine: $375 mandatory, $1,075 maximum Court may order house arrest, clinical assessment, participation in a drug education/treatment program, work release, community service, probation or more. License suspension: 30 days |
| Oklahoma | Zero tolerance law | Imprisonment: 10 days to 1 year
Fine: $1,000 maximum Required to have a drug assessment/evaluation and comply with all recommendations made |
| Oregon | Under the influence DUID | Fine: $1,000 minimum, plus conviction fee of $255 |
| Pennsylvania | Zero tolerance law | License suspension: 1 year
Imprisonment: 3 days to 6 months Fine: $1,000 to $5,000 Must attend alcohol safety school and treatment if ordered |
| Rhode Island | Under the influence DUID | Fine: $100 to $300
Public community restitution: 10 to 60 hours and/or imprisonment of up to 1 year License suspension: 30 to 180 days May be required to attend a course on driving while intoxicated Ignition interlock may be required |
| South Carolina | Under the influence DUID | Fine: $400
Imprisonment: 2 to 30 days or 48 hours of public service employment |
| South Dakota | Zero tolerance law | License revocation: 30 days to 1 year, except for employment, 24/7 sobriety testing, attendance at school, child care delivery or pickup or attendance at counseling programs |
| Tennessee | Under the influence DUID | Fine: $350 to $1,500
Imprisonment: 2 days to 11 months License revocation: 1 year but can have restricted license Mandatory participation in a drug treatment program Ignition interlock device required |
| Texas | Under the influence DUID | Fine: $2,000 maximum
Imprisonment: Mandatory 3 days, 180 days maximum Driver’s license revocation: 1 year maximum |
| Utah | Zero tolerance law | Imprisonment: 364 days maximum
Fine: $25,000 maximum |
| Vermont | Under the influence DUID | Imprisonment: 2 years maximum
Fine: $750 maximum May be required to participate in community service, drug education/treatment program, victim restitution or more License suspension: 90 days mandatory |
| Virginia | Under the influence DUID | License suspension: 1 year |
| Washington | Per se law; cannot have a THC concentration of 5 ng/mg or higher within 2 hours of driving | Imprisonment: 1 year maximum
Fine: $5,000 maximum Court may require community service, victim restitution, victim compensation fund, house arrest or more |
| Washington D.C. | Under the influence DUID | $1,000 fine, 180-day maximum imprisonment or both |
| West Virginia | Under the influence DUID | Imprisonment: 6 months maximum
Fine: $100 to $500 |
| Wisconsin | Zero tolerance law | Fine: $150 to $300
License revocation: 6 to 9 months |
| Wyoming | Under the influence DUID | 6 months maximum imprisonment, $750 maximum fine or both
Must receive and pay for substance abuse assessment |
How Impairment Is Measured
THC concentrations are measured in blood and urine tests. Some states, such as Alabama, are piloting oral fluid testing — which consists of testing saliva for its THC content.3
Alcohol vs. Marijuana-Impaired Driving
While driving under the influence of alcohol has proven consistently to be dangerous, the results of driving under the influence of marijuana are not as clear-cut. A person’s tolerance, smoking technique and absorption of THC cause a variety of effects that aren’t as uniform as the consequences of drinking alcohol.
However, according to the National Library of Medicine, marijuana causes more detriment to automatic driving functions, whereas alcohol affects more complex tasks. While people high on marijuana can compensate effectively, combining alcohol and marijuana makes driving safely dangerous and difficult. Still, as the organizations and studies cited below suggest, it’s not clear if marijuana usage on its own causes more accidents, even though alcohol does.
How Cannabis Impairs Driving: Is It Safe to Drive High?
Does marijuana affect your ability to drive? While this may sound like a silly question with an obvious answer, science isn’t so sure about the dangers of driving while high. Cannabis users, read this before you get into your motor vehicle after lighting up.
Historically, national institutions like the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention have found that driving while high impairs coordination, distorts perception and makes short-term memory and problem-solving difficult. This leads to more car crashes4. The National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA) seconds this data.
However, a recent study from the Canadian Institute of Actuaries and the Casualty Actuarial Society analyzed both Canadian and United States data about collision or private vehicle losses in fatal accidents from 2016 to 2019. While they found that marijuana impacts driving behavior, it didn’t necessarily increase risk. In some cases, marijuana usage led people to drive slower and have longer following distances.5
Another study from the National Institute of Justice and RTI International found little correlation between THC levels and impaired driving. It concluded that THC levels don’t indicate marijuana ingestion reliably. While field tests for alcohol measure impairment, marijuana intoxication isn’t so easily measured.6
Signs of Marijuana Impairment While Driving
According to the NIDA, the following driving behaviors are signs of marijuana impairment.
- More lane weaving
- Slow reaction time
- Less attention to the road7
But due to conflicting study results, more research is needed to determine the relationship between THC levels and impaired driving.
Impaired Driving Statistics
Unfortunately, the statistics available on marijuana impairment while driving are lacking. The most recent data is from 2018, already five years old at the time of this writing. Still, we have some insight into how often people ingest marijuana before getting behind the wheel.
An analysis of National Highway Traffic Safety Administration’s Fatality Analysis Reporting System (FARS) data by the Governors’ Highway Safety Administration reveals the number of people killed in car accidents who were under the influence of alcohol or drugs.
| Percentage of fatally injured drivers by known test results | 2006 FARS Final File | 2015 FARS Final File | 2015 FARS Annual Report | 2016 FARS Annual Report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alcohol | 41% | 28% | 38% | 38% |
| Drug | 28% | 43% | 43% | 44% |
The difference between the FARS Final Files and Annual Reports is that the Annual Reports may have outside variable data, which may lead to data differences in the final counts. These revisions are typically minor, however.8
But keep in mind that the category of drugs here doesn’t only refer to marijuana but also opioids, hallucinogens and other illegal drugs.
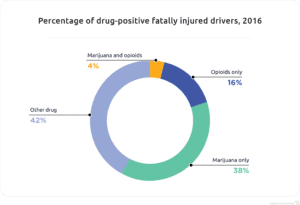
That said, when comparing marijuana usage to opioids, more people killed in car crashes in 2016 tested positive for marijuana only (38 percent) than opioids. However, 42 percent tested positive for another drug besides marijuana or opioids, which could refer to a wide range of substances.9
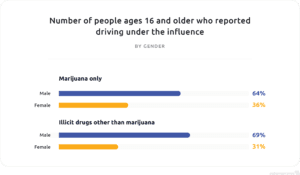
CDC data shows that, as of 2018, 64 percent of those who reported driving under the influence of marijuana were male while only 36 percent were female. For drugs other than marijuana, such as cocaine, heroin, inhalants, hallucinogens and methamphetamines, the gender difference was even more stark.
DID YOU KNOW?
In general, men pay more for car insurance due to their higher chance of driving under the influence and getting into accidents, resulting in costly claims.
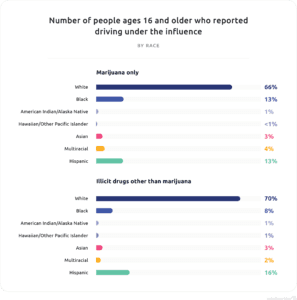
The majority of people who reported driving under the influence of marijuana (66 percent) were white, followed by Black and Hispanic people (tied for second at 13 percent). White people also were most likely to drive while under the influence of other drugs at 70 percent, compared to only 16 percent of Hispanic people and 8 percent of Black people.
Safety Tips: How to Prevent Impaired Driving
It’s easy to prevent impaired driving: Don’t drive while impaired, even if you think you can. Let’s break this down:
- Don’t drive after any marijuana use.
- Don’t let your friends and family drive after any marijuana use.
- Instead, use a designated sober driver.
- Alternatively, use a rideshare service or public transportation to get to your destination.
Conclusion
While it’s not conclusive what effects marijuana usage has on driving behaviors, it’s best not to drive high — for safety reasons and because every state has laws against it. Instead, always get behind the wheel sober and focused, making sure you have the energy and focus you need to drive defensively.
Citations
Drugged Driving | Marijuana-Impaired Driving. NCSL. (2022, Nov 11).
https://www.ncsl.org/transportation/drugged-driving-marijuana-impaired-drivingTetrahydrocannabinol (THC). National Library of Medicine. (2023, May 2).
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK563174/Oral Fluid Drug Testing Program. ADFS. (2023).
https://adfs.alabama.gov/services/tox/toxicology-oral-testing-programMarijuana and Driving: How to Keep Your Fleet’s Drivers Safe. CDC. (2021, Nov 23).
https://www.cdc.gov/niosh/newsroom/feature/marijuana-and-driving.htmlAssessing the Impact of Marijuana Decriminalization on Vehicle Accident Experience. Casualty Actuarial Society. (2022, Dec).
https://www.casact.org/sites/default/files/2022-12/Marijuana-Decriminalization_Report.pdfField Sobriety Tests and THC Levels Unreliable Indicators of Marijuana Intoxication. NIJ. (2021, Apr 5).
https://nij.ojp.gov/topics/articles/field-sobriety-tests-and-thc-levels-unreliable-indicators-marijuana-intoxicationDrugged Driving DrugFacts. NIH. (2021, Apr 5).
https://nida.nih.gov/publications/drugfacts/drugged-drivingTraffic Safety Facts Annual Report Tables. NHTSA. (2022, Jun 24).
https://cdan.nhtsa.gov/tsftables/tsfar.htmDrug-Impaired Driving: Marijuana and Opioids Raise Critical Issues for States. GHSA. (2023).
https://www.ghsa.org/resources/DUID18
